
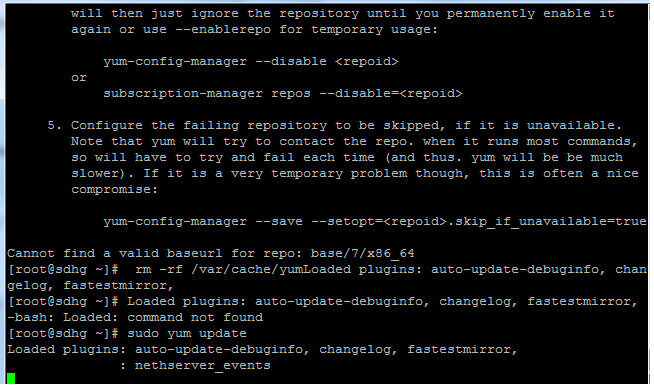
# subscription-manager config -rhsm.manage_repos=0 This default redhat.repo repository can be disabled by editing the Subscription-Manager configuration and setting the manage_repos value to zero (0). It can create static in content management operations if that repository is not the one actually used for subscriptions, such as for a disconnected system or a system using a local content mirror. Maintaining a redhat.repo file may not be desirable in some environments. When a system is registered using Subscription-Manager, the rhsmcertd process creates a special yum repository - redhat.repo. User may encounter dependency issues if a package being updated by the base repo, requires the package from the disabled repo to update as well Disabling the Subscription-Manager Repository Note: if another update is released in the disabled repo, the system will not apply that update unless enabling the repository again. For example: # yum install rubygems -enablerepo=rhel-6-server-optional-rpms Note: yum-config-manager is only available for RHEL 6 and later # yum install -y yum-utilsĮnable a repository for a single yum transactionĪ repository may be temporarily enabled by using the -enablerepo= option. The repositories can be enabled or disabled using the yum-config-manager command, which is provided by the yum-utils package: Using Yum-Utils provided yum-config-manager: To disable a specific Red Hat repository: # subscription-manager repos -disable=rhel-6-server-optional-rpms To enable a specific Red Hat repository: # subscription-manager repos -enable=rhel-6-server-optional-rpms To see a list of available repositories: # subscription-manager repos -list Subscription-manager provides its own utility to enable & disable repositories ONLY within the redhat.repo file: Rhel-6-server-extras Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6Server - Extras disabled

Rhel-6-server-optional-rpms Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6Server - Optional disabled Rhel-6-server Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6Server enabled List all available repositories for the system, including disabled repositories: # yum repolist all The content repositories are based on the product and on the content delivery network, defined in the baseurl parameter of the nf file.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
